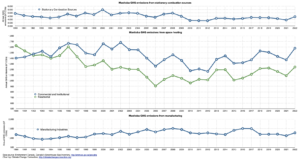
In 2022, stationary combustion sources accounted for about 20% of Manitoba’s greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (1).
Most of these emissions are from heating our buildings.
Stationary sources include energy used in
- residential and commercial heating
- manufacturing and construction industries
- electricity generation
- mining/oil and gas extraction
Figure 1 shows how these emissions have changed from 1990 to 2021:
- 10.1% decrease overall from Stationary Combustion
- 23.4% decrease in residential heating – mostly due to success of programs to reduced demand (e.g. insulation, furnace replacement)
- 12.6% increase from Commercial & institutional
- 7.9% increase from Manufacturing industries
To download a PDF file with the data, click here: Manitoba_GHG_trend_chart_1990-2022_stationary.pdf (132KB)
NOTE: All data are in CO2 equivalent kilotonnes per year. (1 kilotonne = 1000 tonnes = 1 million kilograms)